Geometric coordinates
A complete guide to understanding spatial representation
Geometric coordinates are the basis of almost every system used to represent space today, whether you’re mapping out a city, creating a videogame, analysing data, or learning geometry at school. They allow us to precisely locate points, describe forms, perform transformations and understand how objects are related in two- and 3-dimensional space.
This article provides a complete and user-friendly overview of the types, applications and mathematical significance of geometric coordinates.
What are Geometric Coordinates ?
A coordinate is an array of numerical values which describe the location of any point in space. The number of values is determined by the size of the system.
- 2D Coordinate (x,y)
- 3D coordinate – (x, y, z)
- Higher dimensions – (x1, x2, x3, …)
The coordinates are a way to express something abstract, like “a point on the plane”, in a way that computers, formulas, and diagrams can understand.
A brief history of Coordinate Geometry
Rene Descartes developed the use of coordinates in geometry during the 17th century. The Cartesian Coordinate System is his invention. It combines algebra and geometry in a powerful framework.
Before coordinates
- Euclid’s geometry was a visual and synthetic form of geometry
- Diagrams and logical steps were used to solve problems
After coordinates:
- Equations can be used to express geometry
- Algebra can be used to analyze curves, lines and shapes
This innovation gave rise to analytic geometries which led to calculus, physics modelling, engineering design and computer graphics.
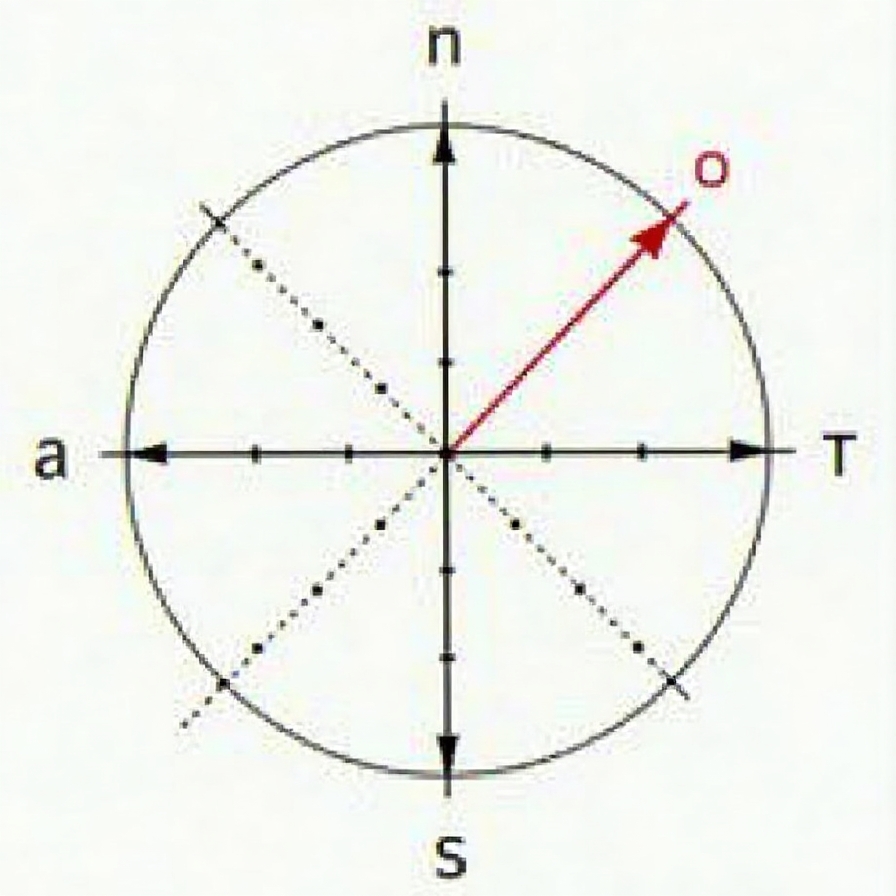
Types and Geometric Coordinate Systems
1. Cartesian Coordinates
The most common system is based on perpendicular axes.
- x-axis — horizontal
- vertical y axis
- z-axis — depth (in 3D)
Features:
- Origin at (0.0) or (0.0.0)
- Distance formula can be used to find distance between two points
- Equations can be used to graph shapes (e.g. circles, lines, and parabolas).
Cartesian coordinates is used for:
- Geometry classes
- Calculators that graph data
- Engineering diagrams
- Computer Graphics
2. Polar Coordinates
Polar coordinates are used instead of x and y to describe a point.
- distance from origin
- angle of reference to
The point is written (r, th).
Example:
- The point (5, 60deg), is located 5 units away from the origin and at a 60deg angular angle.
Polar coordinates can be used for a variety of purposes.
- Circles
- Spiral patterns
- Navigation systems
- Problems of rotational physics
3. The Cylindrical Coordinate System and the Spherical Coordinate System
Alternative coordinate systems in 3D space can simplify some problems.
Cylindrical (r th z) — Combines polar coordinates and height
Spherical (r th ph) — Uses radii and angle to represent positions on spheres
The following systems are commonly found:
- Astrophysics
- Electromagnetics
- 3D modeling
- Robotics
How coordinates are used in Geometry
1. Descripting shapes
The coordinates are used to describe shapes precisely, for example:
- A line: y = mx + b
- A circle: (x-h)2 + y-k)2 = R2
- A polygon is a sequence of vertices (x1,y1), (x2,y2) and…
This eliminates any ambiguity, and allows for precise measurements.
2. Measurement of Distance and Midpoints
The formula for distance is an application of Pythagorean theory:
[
d = (x_2 — x_1)2 + y_2 — y_12
]
The formula can be used to find the exact midpoint between two points.
[
M = left (fracx_1+ x_22; fracy_1+ y_22right).
]
They are indispensable tools for geometry, physics and computer graphics.
3. Transformations
Geometric transformations are made easy by coordinates.
- Translation: (x + a, y + b)
- Rotation : using rotation matrixes
- Reflexion: Flipping across axes
- Scaling : multiplying coordinates
Animation and 3D modelling is built on these principles.

Real World Applications of Geometric Coordinates
1. GPS and Mapping
GPS triangulates coordinates on the Earth’s surface using satellites.
- Latitude/longitude (spherical)
- UTM (Cartesian)
- State coordinate systems
Modern navigation is impossible without coordinates.

2. Computer Graphics and Gaming
Video games
- Each object has coordinates
- Geometric calculations are essential for movement and physics
- Coordinate transformations are used by 3D engines like Unity and Unreal.
3. Architecture and Engineering
Coordinates are used in both blue prints and CAD software to ensure accuracy.
- Measurements
- Dimensions
- Placement of structural components
4. Robotics & AI
Robot navigation using:
- Maps of coordinates
- Position tracking
- Spatial Modeling
Real-time coordinate geometries are essential for machine vision and autonomous drones.
Why Geometric Coordinates are Important in Mathematics
Geometric coordinates are a bridge between algebra, and geometry. They help students to convert visual ideas into numerical relationships. Students can:
- Visualize algebraic equations
- Geometric problems solved with precision
- Understanding space in an analytical way
The mastery of coordinate systems is the key to higher level math.
- Calculus
- Linear algebra
- Differential geometry
- Vector Analysis
Conclusion
Geometric coordinates go beyond numbers. They are fundamental to how we perceive and manipulate the space around us. They are a universal language that describes the world we live in.
Understanding geometric coordinates can be essential to solving problems and fostering innovation in a wide range of fields, whether you are a student or developer.



